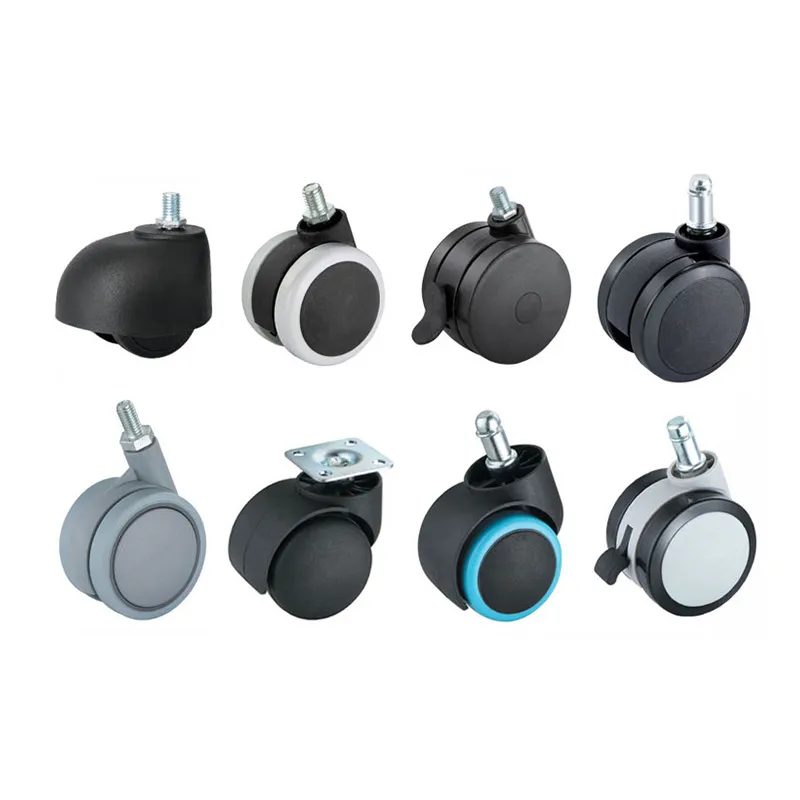
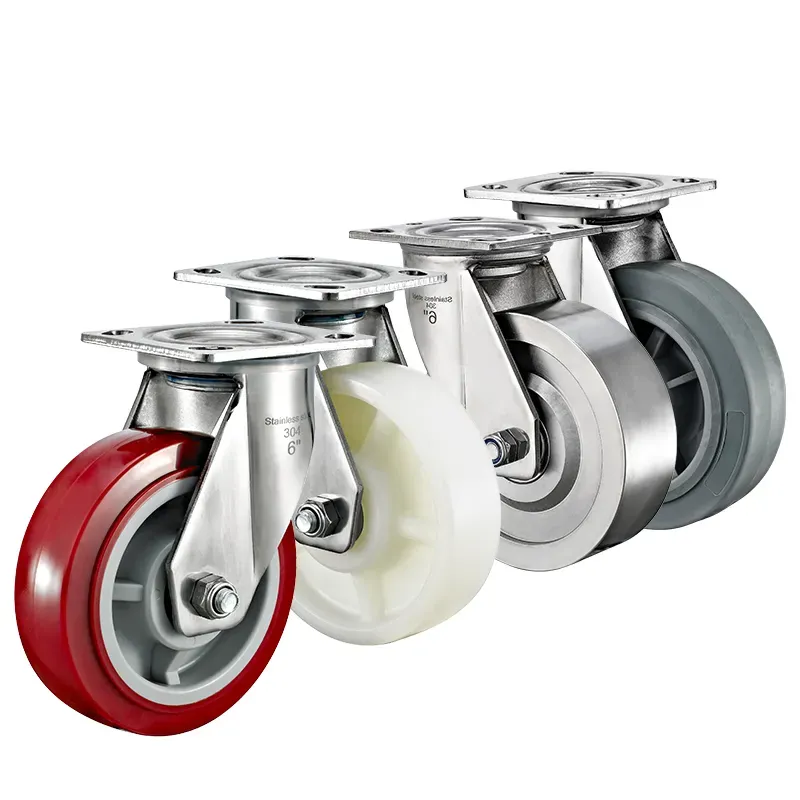
Tabla de tamaños de ruedas giratorias
¡Encuentre su rueda perfecta sin esfuerzo!
Bienvenido a nuestra intuitiva tabla de parámetros de ruedas. Con solo unos pocos clics, descubra ruedas que se ajusten exactamente a sus necesidades. Nuestra tabla muestra características clave, lo que garantiza que usted tome decisiones informadas de forma rápida y sencilla. Pero recuerda, ¡esto es sólo la punta del iceberg! Tenemos una amplia gama de opciones más allá de las enumeradas. ¿Desea más detalles o necesita una solución personalizada? ¡Comuníquese con nosotros! Nuestro equipo está listo para proporcionar parámetros integrales y cotizaciones competitivas, adaptando soluciones perfectamente adaptadas a sus requisitos únicos. ¡Caminemos juntos hacia la perfección!
| 1 | Diámetro de rueda/pulgada | Diámetro de la rueda/mm | Ancho de rueda/mm | Material | Carga/kg | Carga/libras |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5 | 40 | 40 | PÁGINAS | 25 | 55 | |
| 2 | 50 | 47 | PÁGINAS | 25 | 55 | |
| 2 | 50 | 38 | TPR | 38 | 90 | |
| 2 | 50 | 24 | PVC+PU | 40 | 90 | |
| 2.5 | 65 | 30 | PVC+PU | 60 | 130 | |
| 3 | 75 | 58 | TPR | 58 | 130 | |
| 4 | 100 | 62 | TPR | 62 | 140 | |
| 2 | 50 | 46 | PÁGINAS | 40 | 90 | |
| 2.5 | 65 | 48 | PP+PU | 45 | 100 | |
| 2.5 | 65 | 48 | PP+TPR | 45 | 100 | |
| 3 | 75 | 60 | PÁGINAS | 70 | 160 | |
| 3 | 75 | 58 | PP+TPR | 60 | S | |
| 4 | 100 | 70 | PP+TPR | 80 | 180 | |
| 5 | 125 | 80 | PP+TPR | 100 | 220 | |
| 5 | 125 | 32 | PP+TPR | 135 | 300 | |
| 6 | 150 | 50 | PU | 450 | 1000 | |
| 8 | 200 | 50 | PU | 550 | 1200 | |
| 4 | 100 | 50 | HIERRO+PU | 300 | 650 | |
| 5 | 125 | 50 | HIERRO+PU | 350 | 800 | |
| 6 | 150 | 50 | HIERRO+PU | 450 | 1000 | |
| 8 | 200 | 50 | HIERRO+PU | 550 | 1200 | |
| 4 | 100 | 50 | TPR | 300 | 650 | |
| 5 | 125 | 50 | TPR | 350 | 800 | |
| 6 | 150 | 50 | TPR | 450 | 1000 | |
| 8 | 200 | 50 | TPR | 550 | 1200 |
Preguntas frecuentes
Para obtener más información sobre las ruedas, no dude en Contáctenos para obtener soluciones y cotizaciones sobre ruedas.
Elegir las ruedas giratorias adecuadas para sus necesidades específicas implica varios pasos clave. Aquí hay una guía profesional paso a paso para ayudarlo a tomar una decisión informada:
Paso 1: determinar la capacidad de carga
– **Calcular Carga Total**: Evalúa el peso total del equipo o mueble que soportarán las ruedas. Esto incluye el peso del objeto en sí más cualquier carga adicional que pueda transportar.
– **Dividir por la cantidad de ruedas**: divida la carga total por la cantidad de ruedas que planea usar. Esto le proporciona la capacidad de carga mínima por rueda.
– **Incluya un margen de seguridad**: elija siempre ruedas con una capacidad que exceda su necesidad calculada en al menos un 25 % a un 30 % para garantizar la seguridad y la longevidad.
Paso 2: evaluar el tipo de piso
– **Material de la superficie**: considere el tipo de piso sobre el que se utilizarán las ruedas. Las ruedas duras generalmente son mejores para superficies blandas como alfombras, mientras que las ruedas blandas son preferibles para superficies duras como baldosas o madera dura para evitar daños al piso.
– **Condición del piso**: tenga en cuenta las condiciones del piso, como grietas, escombros o superficies irregulares, que puedan afectar el rendimiento de la rueda.
Paso 3: elige el material de la rueda
– **Ruedas de poliuretano**: Excelentes para una variedad de superficies, ofrecen una buena protección del piso y son duraderas.
– **Ruedas de goma**: Proporcionan un funcionamiento suave y silencioso y son buenas para la absorción de impactos.
– **Ruedas de nailon o plástico**: Adecuadas para aplicaciones livianas, generalmente menos costosas.
– **Ruedas de acero o hierro fundido**: Ideal para aplicaciones industriales de alta capacidad, especialmente donde la protección del piso no es una preocupación.
Paso 4: decidir el tamaño de la rueda
– **Ruedas más grandes**: ruedan más fácilmente y son mejores para superficies o umbrales irregulares.
– **Ruedas más pequeñas**: más compactas y mantienen la altura total más baja, pero pueden ser más difíciles de rodar en superficies irregulares.
Paso 5: considere las opciones de montaje
– **Soportes de vástago**: Bueno para aplicaciones ligeras a medianas, fácil de instalar.
– **Montajes de placa**: Proporcionan más estabilidad, adecuados para cargas más pesadas.
Paso 6: piense en la maniobrabilidad
– **Ruedas giratorias**: ofrecen un movimiento completo de 360 grados, ideal para espacios reducidos.
– **Ruedas fijas/rígidas**: solo se mueven en línea recta, pero son más estables cuando se desplazan en línea recta.
Paso 7: evaluar las características especiales
– **Frenos o bloqueos**: Esenciales para aplicaciones donde la rueda necesita permanecer estacionaria en ocasiones.
– **Condiciones ambientales**: si se usa en exteriores o en ambientes hostiles, considere materiales resistentes a la intemperie como el acero inoxidable.
Paso 8: Cumplimiento y Estándares
– Verifique los estándares o requisitos de cumplimiento específicos de la industria, especialmente en entornos comerciales o industriales.
Paso 9: Consulta con un especialista
– Si no está seguro, busque el asesoramiento de un especialista en ruedas giratorias que pueda brindarle recomendaciones personalizadas basadas en sus requisitos específicos.
Si sigue estos pasos, podrá elegir ruedas giratorias que se adapten bien a su aplicación, garantizando un rendimiento, seguridad y longevidad óptimos.
Hay varios tipos de ruedas disponibles, cada una diseñada para aplicaciones y entornos específicos. Comprender los diferentes tipos puede ayudarle a elegir el más adecuado para sus necesidades. Estos son algunos de los tipos comunes de ruedas:
1. **Ruedas giratorias**: Estas ruedas pueden girar 360 grados, lo que permite girar y maniobrar fácilmente en cualquier dirección. Son ideales para carros y equipos que requieren cambios frecuentes de dirección.
2. **Ruedas rígidas o fijas**: Estas ruedas no giran y solo se mueven en línea recta. Por lo general, se usan cuando se necesita un movimiento en línea recta y, a menudo, se combinan con ruedas giratorias para brindar estabilidad y control.
3. **Ruedas con freno**: Estas ruedas vienen con un mecanismo de freno que puede bloquear la rueda en su lugar. Son útiles en aplicaciones donde el equipo necesita permanecer estacionario durante su uso.
4. **Ruedas neumáticas**: Estas ruedas tienen neumáticos llenos de aire y brindan una marcha amortiguada, lo que las hace adecuadas para uso en exteriores o sobre superficies irregulares. Absorben bien los golpes y vibraciones.
5. **Ruedas con resorte**: Diseñadas para absorber impactos y reducir el ruido, estas ruedas son ideales para equipos sensibles a la vibración o que deben transportarse suavemente sobre superficies rugosas.
6. **Ruedas de acero inoxidable**: Son resistentes a la corrosión y se utilizan a menudo en entornos donde la limpieza y la higiene son importantes, como en aplicaciones médicas o de servicios alimentarios.
7. **Ruedas de servicio pesado**: Fabricadas para ofrecer resistencia y durabilidad, estas ruedas pueden soportar un peso considerable y se utilizan a menudo en entornos industriales.
8. **Ruedas con ranura en V**: Diseñadas para pistas o ranuras en el piso, estas ruedas guían el equipo a lo largo de una trayectoria predeterminada, comúnmente utilizada en entornos industriales o de fabricación.
9. **Ruedas de poliuretano**: Fabricadas con una banda de rodadura de poliuretano, estas ruedas son conocidas por su durabilidad, protección del piso y funcionamiento silencioso. Son versátiles para su uso en diversos entornos.
10. **Ruedas de goma**: Ideales para proteger pisos y reducir el ruido, las ruedas de goma se usan comúnmente en entornos institucionales, como escuelas y hospitales.
11. **Ruedas de nailon o plástico**: Generalmente es más asequible y adecuado para aplicaciones ligeras. Funcionan bien en superficies lisas y duras.
Cada tipo de rueda tiene sus ventajas específicas y está diseñada para cumplir con diferentes requisitos funcionales, como capacidad de carga, tipo de piso, condiciones ambientales y necesidades de maniobrabilidad.
Utilice la calculadora de carga de ruedas en línea.
Calcular la capacidad de carga de las ruedas es un paso crucial para garantizar que las ruedas que elija puedan soportar de manera segura y efectiva el peso de su equipo o muebles. A continuación se explica cómo calcularlo:
1. Determine el Peso Total a Soportar:
– Sume el peso del equipo o mueble al que se unirán las ruedas.
– Incluir la carga máxima que soportará el equipo o mobiliario.
2. Decidir el número de ruedas:
– Determine cuántas ruedas utilizará para el equipo. Las configuraciones comunes incluyen cuatro o seis ruedas, pero esto puede variar según el diseño y los requisitos.
3. Calcule la capacidad de carga por rodaja:
– Divida el peso total por el número de ruedas.
Por ejemplo: si un equipo pesa 400 libras y soporta 100 libras adicionales, el peso total es 500 libras. Si planea usar cuatro ruedas, entonces cada rueda debe soportar al menos 125 libras (500 libras ÷ 4 ruedas).
4. Incluya un margen de seguridad:
– Es importante agregar un margen de seguridad a sus cálculos. Una práctica común es agregar entre un 25 y un 30 % a la capacidad de carga por rodaja. Esto explica cualquier distribución desigual del peso y cargas inesperadas.
– Siguiendo con el ejemplo, si cada rueda necesita soportar 125 libras, agregar un margen de seguridad del 30 % significaría elegir ruedas que puedan soportar al menos 162,5 libras cada una (125 libras × 1,30).
5. Considere las condiciones de operación:
– Si las ruedas se utilizarán en condiciones difíciles (como superficies rugosas, movimientos frecuentes o exposición a productos químicos), es posible que necesite ruedas con una mayor capacidad de carga.
6. Seleccione ruedas según la capacidad de carga calculada:
– Elija ruedas que cumplan o superen la capacidad de carga calculada por rueda, incluido el margen de seguridad.
Al calcular cuidadosamente la capacidad de carga y considerar el margen de seguridad y las condiciones de operación, puede asegurarse de que sus ruedas sean seguras y efectivas para sus necesidades específicas.