캐스터가 어떤 부품으로 만들어 졌는지 아십니까?
캐스터의 각 부분의 기능을 알고 있습니까?
이 기사에서는 Caster Wheel Assembly를 자세히 소개합니다.
아래 그림을보십시오. 우리는 일본어를 사용합니다 대형 산업 캐스터 설명으로. 현재 시장에 나와있는 산업용 캐스터는 구조가 동일하며 일반적인 산업 캐스터 어셈블리로 간주 될 수 있습니다.
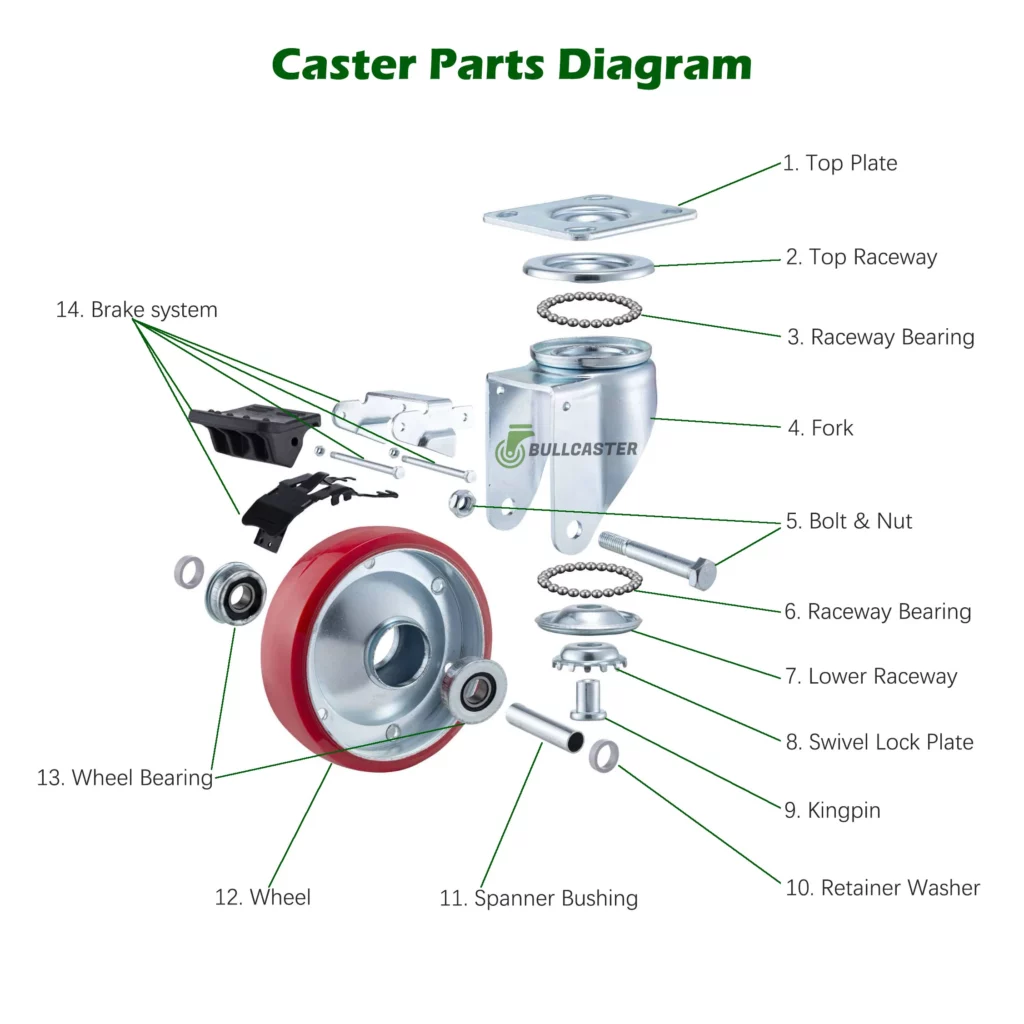
캐스터 휠 부품 소개
A. 캐스터 휠 탑 플레이트 (1)
상단 플레이트는 캐스터의 장착 플레이트이며 캐스터 브래킷의 일부입니다. 캐스터의 설치를 용이하게하기 위해 상단 플레이트에 일반적으로 4 또는 6 개의 준비된 구멍이 있습니다.
캐스터 휠 탑 플레이트 외에도 Casters는 STEM, BOLT HOLE, EXPAND STEM, RIGID 등과 같은 다양한 장착 방법을 가지고 있습니다. 이전 기사를 읽을 수 있습니다. 캐스터 장착 유형.
상단 플레이트의 두께는 캐스터의 하중을 함유하는 용량의 결정 요인 중 하나라는 점은 주목할 가치가 있습니다. 일반적으로 사용자의 요구에 따라 캐스터 브래킷과 상단 플레이트의 두께가 두껍게됩니다. 캐스터의 부하 용량.
B. 캐스터 레이스 웨이 및 레이스 웨이 베어링 (2.3.6.7)
캐스터 휠 레이스 웨이는 스위블 캐스터의 구성 요소입니다. 캐스터 휠의 경마장은 본질적으로 캐스터의 고정 부분과 회전 부분 사이의 인터페이스입니다. 두 가지 주요 부분으로 구성됩니다.
- 내부 경마장:이 부분은 캐스터의 줄기 또는 장착 플레이트에 부착되어 있으며 고정 상태로 유지됩니다.
- 외부 경마장:이 부분은 휠 어셈블리에 부착되어 있으며 회전하거나 스파이되는 부분입니다.
이 두 경마장 사이에는 일반적으로 볼 베어링이나 롤러 베어링이 될 수있는 베어링이 있습니다. 이 베어링은 캐스터의 고정 부분에 비해 휠 어셈블리의 부드러운 회전 또는 회전을 용이하게합니다. 경마장을 통해 캐스터는 360도 회전 할 수 있으므로 휠이 방향을 매끄럽게 바꾸고 최소한의 노력으로 변경할 수 있습니다.
작동 방식은 다음과 같습니다.
- 스위블 헤드 : 이것은 경마장이 위치한 캐스터의 상단 부분입니다. 스위블 헤드를 사용하면 캐스터가 수직 축으로 회전 할 수 있습니다.
- 최고 경마장 : 경마장 자체는 볼 베어링이 앉아있는 일련의 원형 트랙입니다. 이 베어링은 최소한의 마찰로 스위블 헤드가 부드럽게 회전 할 수 있도록합니다. 최고 경마장은 종종 강도와 부드러운 회전을위한 더블 볼 경마장입니다.
- 볼 베어링 : 경마장 내에 위치한이 작은 금속 공은 캐스터의 움직이는 부분 사이의 마찰을 줄여서 부드러운 움직임을 촉진합니다.
경마장의 설계 및 구조는 캐스터의 성능과 내구성에 중요합니다. 잘 디자인 된 레이스 웨이는 마찰을 줄여서 더 쉬운 움직임과 더 나은로드 베어링 용량을 허용합니다. 이는 캐스터가 상당한 가중치를 지원하고 이동 해야하는 산업 또는 중장 적 애플리케이션에서 특히 중요합니다.
C. 캐스터 휠 브래킷 포크 (4)
캐스터 휠 브래킷 포크는 휠 볼트, 상단 플레이트 및 캐스터 브레이크 시스템을 연결하는 구조입니다.
그 재료는 일반적으로 강판이며, 표면 처리는 일반적으로 아연 도금, 전기 영동 페인팅, 크롬 도금 등입니다. 일부 고급 요구의 경우, 재료는 다음과 같습니다. 스테인레스 스틸 바.
브래킷 포크의 재료와 두께는 또한 캐스터의 하중 기반 용량에 영향을 미치는 중요한 요소라는 점에 주목할 가치가 있습니다.
D. 볼트와 너트 (5)
볼트와 너트의 주요 기능은 휠과 브래킷이 사용 가능한 캐스터를 형성하도록 캐스터 브래킷에 휠을 설치하는 것입니다. 대형 캐스터는 두껍고 고강도 볼트를 사용해야합니다.
E. 스위블 잠금판 (8)
캐스터 휠 스위블 잠금 플레이트는 캐스터의 스위블 동작을 잠글 수있는 기능을 제공하기 위해 특정 유형의 캐스터에 사용되는 구성 요소입니다. 이 기능은 스위블 캐스터를 일시적으로 또는 영구적으로 강력한 시체로 변환 해야하는 응용 분야에서 특히 유용합니다.
스위블 잠금판을 사용하면 사용자가 캐스터의 스위블 메커니즘을 잠글 수 있습니다. 잠금이 약혼하면 캐스터가 수직 축을 주위로 회전하는 것을 방지하여 스위블 캐스터를 견고하고 비 늑골 캐스터로 변형시킵니다. 이것은 안정성이 필요한 상황이나 캐스터가 편차없이 직선으로 이동 해야하는 상황에서 유용 할 수 있습니다.
F. Kingpin (9)
Kingpin의 기능은 캐스터의 상단 플레이트, 경마장, 포크, 스위블 잠금 및 기타 구성 요소를 결합하여 완전한 캐스터 브래킷을 형성하는 것입니다.
G. 캐스터 휠 베어링 (10.11.13)
캐스터 휠 베어링은 마찰을 줄이기 위해 중요하여 부드럽고 쉬운 휠 회전을 가능하게합니다. 그들은 특히 무거운 하중에서 이동성을 향상시키고 캐스터의 전반적인 하중 기반 용량에 기여합니다. 캐스터 베어링에는 여러 가지 유형이 있습니다. 당신은 내 이전 기사를 확인할 수 있습니다 캐스터 베어링 소개.
H. 캐스터 휠 (10.11.13)
휠은 베어링, 스패너 부싱, 리테이너 세탁기, 볼트 및 너트를 통해 캐스터 브래킷에 설치됩니다.
많은 종류의 바퀴, 재료 및 많은 크기가 있습니다. 다른 요구에 따라 다른 유형의 휠을 선택해야합니다. 당신은 우리를 확인할 수 있습니다 캐스터 재료에 대한 가이드 당신의 요구에 가장 적합한 바퀴를 선택합니다.
I. 캐스터 휠 브레이크 어셈블리 (10.11.13)
caster wheel brake is a mechanism added to a caster to allow it to be locked in place, preventing the wheel from rolling. This feature is essential for ensuring stability and safety, especially in applications where the caster supports heavy loads or is on an incline. The brake can be engaged manually, often with a foot pedal, and when activated, it applies pressure to the wheel or its housing to stop movement. There are different types of caster brakes, including total lock brakes that also lock the swivel action, providing complete immobility of the caster.
If you need to purchase casters, please 불캐스터에게 연락하기 directly, we can provide you with comprehensive casters solutions.


