What is A Caster in Manufacturing?
Casters are wheel and bracket assemblies that are commonly used in a wide range of applications to provide mobility and convenience. They are used in many different industries, including Industrial production, medical industry, furniture industry, retail industry, and logistics industry. Casters can be made from a variety of materials, including plastic, metal, and rubber, and they are available in different sizes and load capacities.
In this article, we will focus on the caster wheel manufacturing process. We will cover the various steps involved in producing casters, including the preparation of raw materials, the manufacturing of caster components, such as wheels and brackets, and the final assembly process. We will also explore the different surface treatment options available for caster components and the importance of quality control measures in ensuring the durability and reliability of casters. By the end of this article, readers will have a better understanding of the complex process involved in producing casters and the various factors that contribute to the quality and performance of these essential components.
How to Make Caster Wheels?
1. Preparation for Casters’ Raw Material
①. Steel sheet
Typically, caster manufacturers use high-quality steel sheets that are specifically designed for industrial use. These steel sheets are made from various grades of steel, including carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel, depending on the specific requirements of the caster being produced.
Generally, the steel sheets used in caster production must meet certain physical and mechanical properties, such as strength, hardness, toughness, and ductility, to ensure that the casters can withstand the stresses and strains of heavy use in industrial applications.
To enhance their durability and performance, the steel sheets used in caster production may be hot-rolled, cold-rolled, or coated with various protective materials, such as galvanized or anti-corrosive coatings.
In addition, the thickness, width, and length of the steel sheets may vary depending on the specific design and size of the caster being produced.
The thickness of the steel plates used in industrial caster production can vary depending on the caster’s specific application and load capacity.
For light-duty casters, which are typically used in applications where the load capacity is less than 500 pounds, the steel plates used may range from 1.5mm (0.059 inches) to 3.0mm (0.118 inches) in thickness.
For heavy-duty casters, which are designed to handle loads of up to 2,000 pounds or more, the steel plates used may range from 3.0mm (0.118 inches) to 6.0mm (0.236 inches) in thickness.
For super heavy-duty casters, which are designed to handle extremely heavy loads of up to 20,000 pounds or more, the steel plates used may range from 6.0mm (0.236 inches) to 10.0mm (0.394 inches) in thickness.
It’s important to note that these are general guidelines and the specific thickness of the steel plates used in caster production can vary depending on the caster design, load capacity, and other factors. It’s always best to consult with a caster manufacturer or supplier to determine the appropriate steel plate thickness for your specific application.
②. Plastic Granules
Plastic granules are small, uniform pellets made from various types of plastic resins, such as rubber, polyethylene, nylon, and polyurethane. These granules are used as the raw material in the injection molding process, which is used to manufacture caster wheels.
The selection of the appropriate plastic granules for caster wheel production depends on several factors, including the desired strength, durability, and flexibility of the caster wheel, as well as the specific application and environmental conditions in which the caster will be used.

For example, polypropylene is a common plastic resin used in caster wheel production because of its durability and resistance to wear and tear. Nylon is another popular option due to its high strength and resistance to impact and abrasion. Polyurethane is also used in some applications because of its high load-bearing capacity and shock absorption properties.
In addition to the specific type of plastic resin used, other factors that can affect the properties of the plastic granules include the size, shape, and color of the pellets. Manufacturers may also add other materials, such as fillers, reinforcements, or additives, to the plastic granules to further enhance their properties and performance.
③. Casters Bering
Bearings are small, precision-engineered components that allow for smooth rotation and movement of caster wheels. They are typically made from steel or other durable materials and come in a range of sizes and styles to accommodate different caster designs and load capacities.
There are several types of bearings that are commonly used in caster production, including:
A. Ball bearings: These are the most common type of bearings used in caster wheels. They consist of a series of small steel balls held in place by a cage, which allows for smooth rolling and rotation of the caster wheel.
B. Roller bearings: These bearings consist of a series of cylindrical rollers arranged in a cage. They are often used in heavy-duty casters because of their ability to support high loads and resist deformation.

C. Tapered roller bearings: These bearings are similar to roller bearings but have a conical shape, which allows them to handle both radial and axial loads.
D. Sleeve bearings: Also known as bushings, these bearings are made from a variety of materials, including bronze, plastic, and self-lubricating composites. They are often used in low-load applications where cost and simplicity are a priority.
In addition to the type of bearing used, other factors that can affect the performance and durability of caster wheels include the bearing size, quality, materials, and lubrication. It’s important to choose the appropriate bearings for the specific application and load capacity of the caster to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
④. Casters Lubricating Oil
Lubricating oil is an essential component in caster production, as it helps to reduce friction and wear between the moving parts of the caster. It is typically made from a blend of base oils and additives, which are chosen based on the specific application and operating conditions of the caster.
The selection of the appropriate lubricating oil for caster production depends on several factors, including the load capacity, speed, temperature, and environmental conditions in which the caster will be used. For example, high-temperature casters may require lubricating oils with a higher viscosity or thermal stability, while wet or corrosive environments may require oils with anti-rust or anti-corrosion additives.

There are several types of lubricating oils that are commonly used in caster production, including:
A. Mineral oil: This is the most basic type of lubricating oil and is typically used in low-load, low-speed applications.
B. Synthetic oil: This type of lubricating oil is designed to perform in high-load, high-speed applications and can withstand extreme temperatures and pressures.
C. Semi-synthetic oil: This type of lubricating oil is a blend of mineral and synthetic oils and is often used in medium to high-load applications.
D. Food-grade oil: This type of lubricating oil is designed for use in food processing and other industries where there is a risk of contamination.
Bullcaster uses the highest quality lubricating oil in the production of casters to ensure the normal operation of the casters.
2. Casters Wheel Manufacturing
①. Injection Molding for plastic wheels
The injection molding process is a commonly used method for producing caster plastic wheels. The process involves several steps, including:
A. Material selection: The first step in the injection molding process is selecting the appropriate plastic material for the caster wheel. The plastic material must meet the necessary strength, durability, and wear resistance requirements. #how to choose caster wheel material.
B. Preparing the mold: The mold is the tool used to shape the plastic material into the desired caster wheel shape. The mold must be designed and fabricated to meet the specific requirements of the caster wheel.
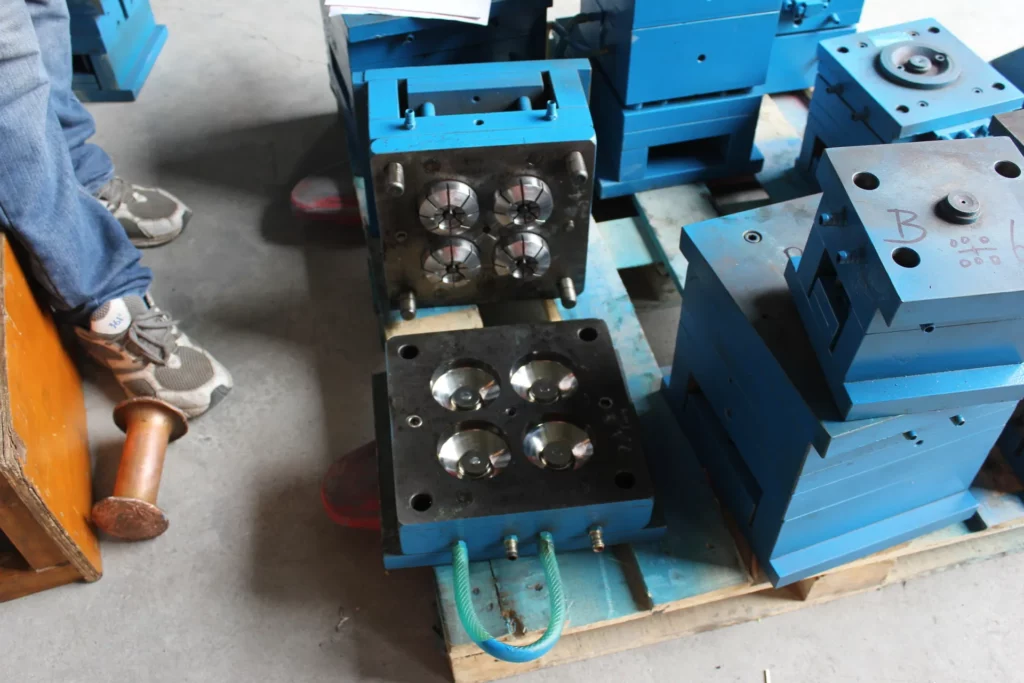

C. Injection molding: The plastic material is melted and injected into the mold under high pressure. The mold is then cooled to solidify the plastic material into the desired caster wheel shape.
D. Ejection: Once the caster wheel has cooled and solidified, it is ejected from the mold. This is done either manually or using an automatic ejection system.
E. Finishing: After ejection, the caster wheel undergoes finishing operations, such as trimming, sanding, or painting. These operations ensure that the caster wheel is of the desired shape, size, and appearance.
F. Quality control: The finished caster wheels undergo quality control checks to ensure that they meet the required specifications and standards. This includes checking for defects such as cracks, warping, or other deformities.
The injection molding process is a fast and efficient method for producing caster plastic wheels with high precision and consistency. It allows for the production of large volumes of caster wheels with minimal waste and can be used to produce caster wheels of varying sizes, shapes, and materials.
②. Cast Iron Craft (Iron Wheel)
The production process of cast iron wheels for casters involves several steps, including:
A. Melting and pouring: The first step in the cast iron production process is melting the iron in a furnace and then pouring it into molds to form the desired wheel shape. The molds are usually made of sand and are designed to create the intricate details and features of the wheel.
B. Cooling and solidifying: Once the molten iron has been poured into the mold, it is left to cool and solidify. During this process, the iron undergoes a phase change from a liquid to a solid state, resulting in the formation of the cast iron wheel.
C. Shakeout and cleaning: After the cast iron wheel has solidified, it is removed from the mold in a process called shakeout. The wheel is then cleaned and any excess material or sand is removed.
D. Machining and finishing: The cast iron wheel undergoes machining operations to remove any excess material and to achieve the desired shape and surface finish. This can involve operations such as turning, milling, and grinding. The wheel is then finished, which may include painting, coating, or polishing to improve its appearance and protect it from corrosion.
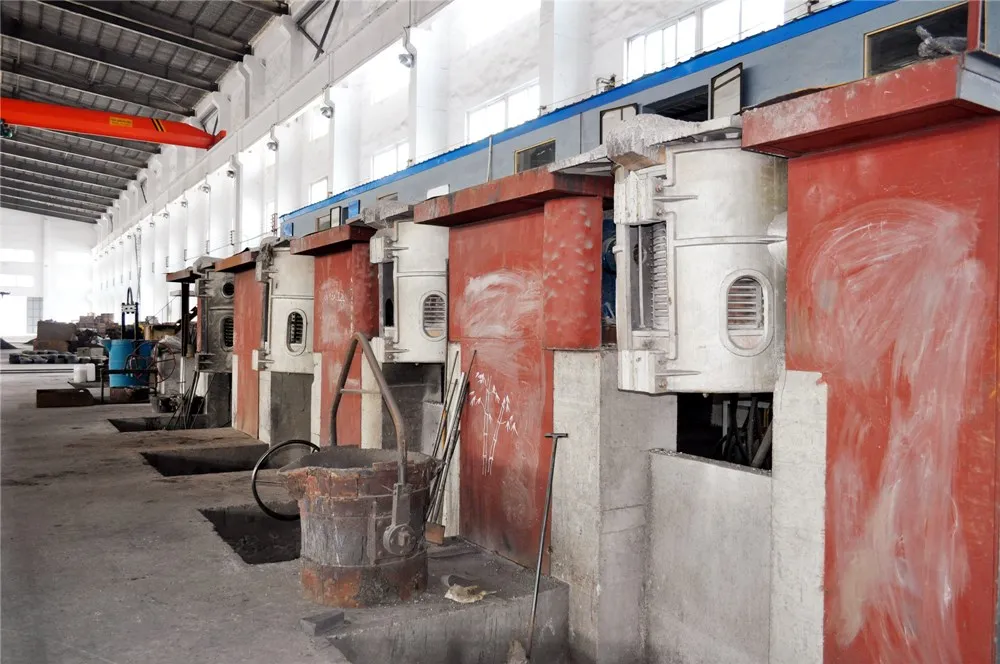

E. Quality control: The finished cast iron wheels undergo quality control checks to ensure that they meet the required specifications and standards. This includes checking for defects such as cracks, porosity, or other deformities.
The production process of cast iron wheels for casters is a time-consuming and labor-intensive process, but it results in wheels that are durable, strong, and capable of withstanding heavy loads and demanding applications. Cast iron wheels are used in a wide range of industries, including manufacturing, warehousing, and transportation, where they provide reliable and long-lasting performance.
③. Stainless Steel Wheels
The production process of stainless steel solid casters involves several steps, including:
A. Material selection: The first step in the production process is selecting the appropriate type of stainless steel for the caster wheel. The stainless steel used for caster wheels must be corrosion-resistant, durable, and able to withstand heavy loads.
B. Casting: The stainless steel is melted in a furnace and then poured into a mold to form the desired wheel shape. The mold is typically made of sand or other materials that can withstand the high temperatures of molten stainless steel.
C. Cooling and solidifying: After the stainless steel has been poured into the mold, it is left to cool and solidify. During this process, the stainless steel undergoes a phase change from a liquid to a solid state, resulting in the formation of the solid caster wheel.

D. Machining: Once the solid caster wheel has solidified, it is removed from the mold and undergoes machining operations to remove any excess material and achieve the desired shape and surface finish. This can involve operations such as turning, milling, and grinding.
E. Finishing: The solid caster wheel is then finished, which may include polishing or buffing to improve its appearance and provide additional corrosion resistance.
F. Quality control: The finished solid caster wheels undergo quality control checks to ensure that they meet the required specifications and standards. This includes checking for defects such as cracks, porosity, or other deformities.
The production process of stainless steel solid casters is a complex and time-consuming process, but it results in caster wheels that are highly resistant to corrosion, durable, and capable of withstanding heavy loads and demanding applications. Solid stainless steel casters are often used in industries such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and clean rooms, where they provide reliable and long-lasting performance in harsh environments.
3. Caster Bracket Manufacturing
The stamping forming process of the caster bracket involves the use of a stamping press to cut and shape sheet metal into the desired bracket shape. The process involves the following steps:
A. Material selection: The first step is to select the appropriate type of sheet metal for the caster bracket. The sheet metal used for the bracket must be strong, durable, and able to withstand the loads and stresses of the caster.
B. Cutting: The sheet metal is cut to the required size using shearing or cutting machines.
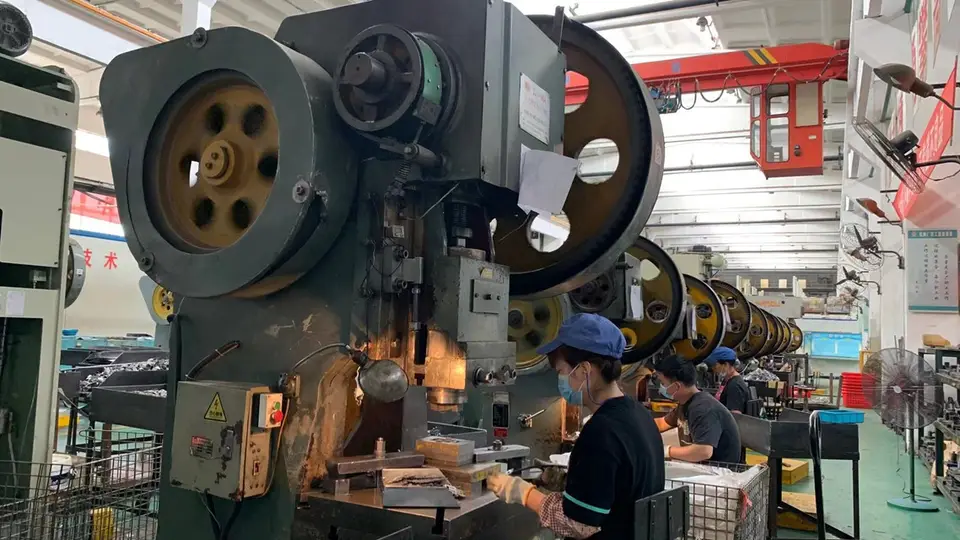

C. Forming: The sheet metal is then fed into the stamping press, where a die and punch are used to shape the metal into the desired bracket shape. The stamping press applies pressure to the metal, forcing it to bend and take the shape of the die.
D. Piercing: Holes are then punched into the bracket using a piercing die, which creates openings for the caster wheel and other components to be attached.
E. Finishing: The bracket is then finished, which may include deburring, polishing, or coating to improve its appearance and provide additional corrosion resistance.
F. Quality control: The finished caster brackets undergo quality control checks to ensure that they meet the required specifications and standards. This includes checking for defects such as cracks, warping, or other deformities.
The stamping forming process is a fast and efficient way to produce caster brackets in large quantities. The resulting brackets are strong, durable, and capable of withstanding the loads and stresses of the caster. Caster brackets are used in a wide range of applications, including furniture, medical equipment, and industrial machinery, where they provide reliable and stable support for caster wheels and other components.
4. Caster Bracket Surface Treatment
The surface treatment process of the caster bracket is an important step in ensuring the bracket’s durability, appearance, and resistance to corrosion and wear. There are several surface treatment options available, including:
A. Electrophoresis: This is a process in which an electric current is used to deposit a thin layer of paint or other coating onto the surface of the bracket. The resulting finish is smooth, durable, and resistant to corrosion.
B. Chrome plating: This involves the electroplating of a thin layer of chromium onto the surface of the bracket. The resulting finish is hard, durable, and highly resistant to corrosion and wear.
C. Galvanizing: This involves coating the bracket with a layer of zinc to protect it from corrosion. The zinc layer acts as a sacrificial anode, corroding in place of the underlying metal.
D. Powder spraying: This involves the application of a dry powder coating onto the surface of the bracket. The powder is electrostatically charged and adheres to the surface of the bracket. The resulting finish is durable and highly resistant to corrosion and wear.
E. Anodizing: This involves the formation of a protective oxide layer on the surface of the bracket by electrochemical means. The resulting finish is hard, durable, and resistant to corrosion and wear.
The choice of the surface treatment process will depend on the application and the desired properties of the bracket. Each process has its advantages and disadvantages, and it is important to select the most appropriate process for the specific requirements of the caster bracket. The surface treatment process is typically the final step in the production of the caster bracket, and it is important to ensure that it is carried out correctly to ensure the longevity and reliability of the caster.
5. Casters Assemble
The assembly process of casters involves combining the various components of the caster, including the wheel, bracket, bearings, and fasteners, to create a functional unit. The process typically involves the following steps:
A. Wheel insertion: The wheel is inserted into the bracket, and the bearings are inserted into the wheel hub.
B. Fastener insertion: The fasteners, such as screws or bolts, are inserted into the bracket to secure the wheel and bearings in place.
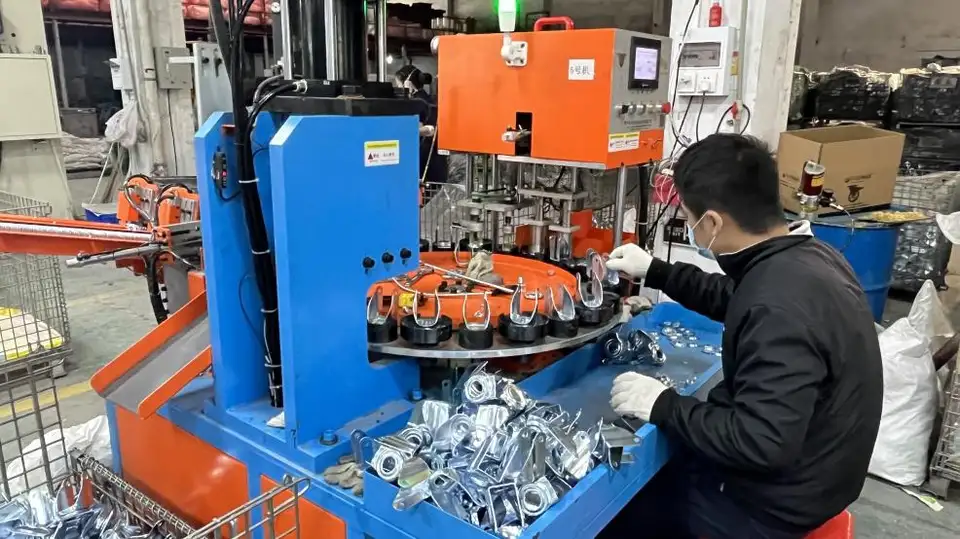

C. Lubrication: The bearings and other moving parts are lubricated to reduce friction and improve the caster’s performance.
D. Final inspection: The assembled caster is inspected to ensure that it meets the required specifications and standards.

E. Packaging: The caster is packaged for shipment, Bullcaster usually packs the casters in cartons + woven bags. When shipping in large quantities, we use plastic pallets to support the casters. Ensure that the casters will not be damaged during transportation.
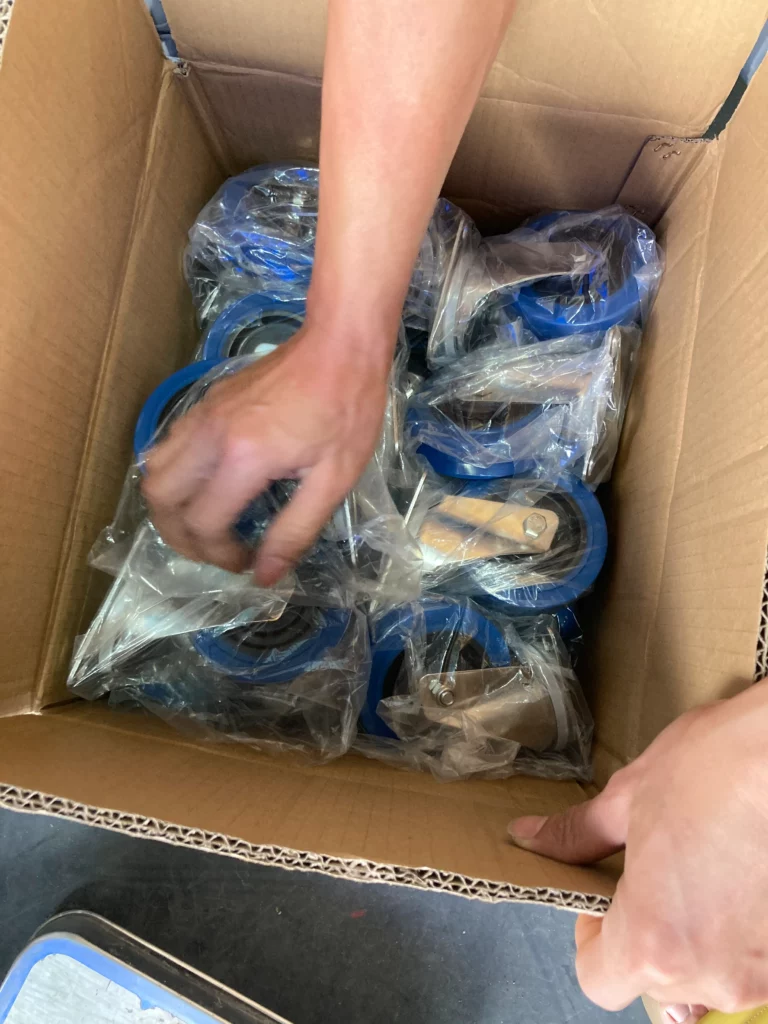

Casters Delivery After Manufacturing
We will make sufficient preparations for each order before delivery, such as freight forwarding arrangements, cargo packing information, cargo marks, customs declaration documents, etc.

We can also help customers handle all customs clearance documents, which mainly depends on the contract In terms of trade if you don’t want to spend too much energy on coordinating the handling of freight forwarding and customs documents, we can help customers handle all customs and customs declaration documents, and you only need to wait for the goods to be delivered to your company’s warehouse.
Who Manufactures Caster Wheels in China?
Bullcaster is a top caster wheel manufacturer in China, We offer industrial casters, medical casters, furniture casters, and stainless steel casters. etc, we can also provide casters’ custom service, you can check our caster products category, just do not hesitate to contact us for any needs. we have more than 800+ casters SKUs that can match your needs.


